rfid access cards bit parity This calculator allows you to manipulate and decode the fields of a standard 26-bit wiegand access card number. You can enter data into any of the fields and the calculator will translate into all other fields. In addition this calculator will generate parity bits (or check the parity if you entered raw card data). Calculator Fields
The NFC antenna on Android phones can vary but is almost always in the middle or upper-middle on the back of the phone. This illustration shows the typical . See more
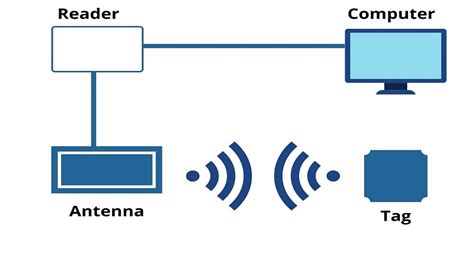
0 · technology behind rfid cards
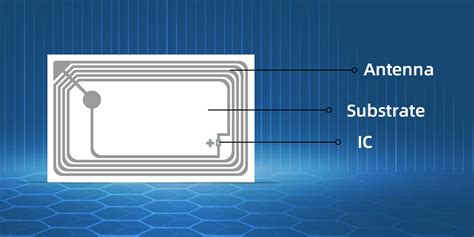
1 · rfid card anatomy
Sep 6, 2022. #2. Try: Signing out your Apple ID on the iPhone. Then use Safari (or any other browser on whatever device) to go to iCloud.com, login with your Apple ID, and go to your .
A NOTE ON PARITY: A parity bit is used as a very simple quality check for the accuracy of the transmitted binary data. The designer of the format program will decide if each parity bit should be even or odd. A selected group of data bits will be united with one parity bit, and the total . Explore the 26-bit Wiegand format, a standard for proximity cards in access .A NOTE ON PARITY: A parity bit is used as a very simple quality check for the accuracy of the transmitted binary data. The designer of the format program will decide if each parity bit should be even or odd. A selected group of data bits will be united with one parity bit, and the total number of bits should result in either an even or odd number. Explore the 26-bit Wiegand format, a standard for proximity cards in access control systems. Understand its encoding, applications, and compatibility with H10301 readers.
Proximity Cards Enable Simple Access. Proximity Cards operate at a frequency of 125 kHz and broadcast a limited amount of data bits designated for personal identification purposes. Bits of data and additional ID numbers are programmed into the card by the card manufacturer.This calculator allows you to manipulate and decode the fields of a standard 26-bit wiegand access card number. You can enter data into any of the fields and the calculator will translate into all other fields. In addition this calculator will generate parity bits (or check the parity if you entered raw card data). Calculator Fields
Almost all access control systems accept the Standard 26-bit Format. The Standard 26-bit Format is an open format. "Open format" means that anyone can buy HID cards in that format. There are 256 possible facility codes. There can be up to 65,535 card ID numbers per facility code.Parity Bits. Thirty-seven bits can be divided up in different ways, which is exactly what was done with the H10304 and H10302 card formats. Both cards include two parity bits as a form of data error checking.
rfid theft protection card
The 26-bit Wiegand format allows for 256 possible facility codes and 65,535 possible ID numbers. When combining both unique identifiers, this allows for 16,711,425 unique access cards. Rather than being written out with numbers or letters as in the example above, the code is represented in an access card or other access device with a series of .Every card is assigned a unique serial number, which is recorded in your access control database and linked to a specific cardholder. For 26-bit cards, the serial number range is from 0 to 65,535. The system reads the card number and checks it against the database to grant or deny access.In simplest terms, the bit format explains how the binary data (0’s and 1’s) on a card are laid out so an access control system can understand them. The total of binary digits is dependent on the formatting, so 26-bits will get you a 26-binary-digit number.The industry’s most common proximity card format is a 26-bit card (also referred to as H10301). This is an open format which allows you as the consumer to order proximity cards from any photo identification retailer.
A NOTE ON PARITY: A parity bit is used as a very simple quality check for the accuracy of the transmitted binary data. The designer of the format program will decide if each parity bit should be even or odd. A selected group of data bits will be united with one parity bit, and the total number of bits should result in either an even or odd number. Explore the 26-bit Wiegand format, a standard for proximity cards in access control systems. Understand its encoding, applications, and compatibility with H10301 readers.Proximity Cards Enable Simple Access. Proximity Cards operate at a frequency of 125 kHz and broadcast a limited amount of data bits designated for personal identification purposes. Bits of data and additional ID numbers are programmed into the card by the card manufacturer.This calculator allows you to manipulate and decode the fields of a standard 26-bit wiegand access card number. You can enter data into any of the fields and the calculator will translate into all other fields. In addition this calculator will generate parity bits (or check the parity if you entered raw card data). Calculator Fields
Almost all access control systems accept the Standard 26-bit Format. The Standard 26-bit Format is an open format. "Open format" means that anyone can buy HID cards in that format. There are 256 possible facility codes. There can be up to 65,535 card ID numbers per facility code.
Parity Bits. Thirty-seven bits can be divided up in different ways, which is exactly what was done with the H10304 and H10302 card formats. Both cards include two parity bits as a form of data error checking.
The 26-bit Wiegand format allows for 256 possible facility codes and 65,535 possible ID numbers. When combining both unique identifiers, this allows for 16,711,425 unique access cards. Rather than being written out with numbers or letters as in the example above, the code is represented in an access card or other access device with a series of .Every card is assigned a unique serial number, which is recorded in your access control database and linked to a specific cardholder. For 26-bit cards, the serial number range is from 0 to 65,535. The system reads the card number and checks it against the database to grant or deny access.In simplest terms, the bit format explains how the binary data (0’s and 1’s) on a card are laid out so an access control system can understand them. The total of binary digits is dependent on the formatting, so 26-bits will get you a 26-binary-digit number.
technology behind rfid cards
1. Fixing the libnfc driver works for this. Here is the fix. To make it work - clone .
rfid access cards bit parity|rfid card anatomy