smart card protocol t1 The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. Although the communication software is tested with TimeCOS, the basic communication protocol (ISO 7816, T = 0) implemented in this application note is common with all smart cards. 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
NFL top-10 rankings: Chiefs top Lions; Steelers, Bills, Eagles climb; Falcons drop out. Check out our guide to the 2024-25 NFL Playoffs including the current bracket and playoff .
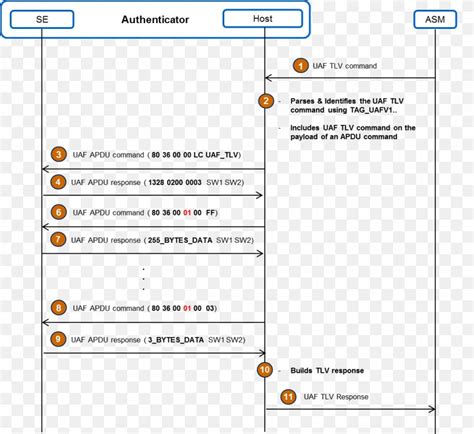
0 · Smart card application protocol data unit
1 · Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level
Here are the steps to copy an RFID card to your iPhone using an NFC writer app: .
I am struggle to understand what protocol I have to use to communicate with the card T0 or T1? So, correct me if I am wrong, but the reader actually decides by itself what protocol to use to communicate with the card if the card supports both. In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the .
passive rfid tags have a power source.
I am struggle to understand what protocol I have to use to communicate with the card T0 or T1? So, correct me if I am wrong, but the reader actually decides by itself what protocol to use to communicate with the card if the card supports both.In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816 -4 Organization, security and commands for interchange . The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports all ISO 7816, EMV™, and GSM11-11 requirements. This one mixed-signal peripheral manages all the details of the interface between a microcontroller and two, independent smart cards.
The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. Although the communication software is tested with TimeCOS, the basic communication protocol (ISO 7816, T = 0) implemented in this application note is common with all smart cards. 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
paul rfid magnetic card case
I have also an ACR38 smart card reader that it support both T=0 and T=1 protocols. (I have T=0 communication with one card successfully and T=1 communication with this card successfully.) I wrote the below program and upload it on the card to send and receive extended APDUs: private ExAPDU() {. Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is a standardized data format and communication protocol used in the interaction between smart cards - in our case, NFC tags - and card readers or host systems.In the context of smart cards, an Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is the unit of communication between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4, which specifies organization, security, and commands for . If the card is able to process more than one protocol type and if one of those protocol types is indicated as T=0, then the protocol type T=0 shall indicated in TD1 as the first offered protocol, and is assumed if no PTS is performed.
passive rfid tag dog tag
This application note describes the fundamentals of the contact type smart cards, and how they are communi-cated using the PIC microcontroller. It also explains the T = 0 and T = 1 protocols, which are widely used in contact type smart card communications.
Michal Bairanzade of ON Semiconductor, describes the basic smart card international specifications and functions, together with the physical interface necessary to handle existing and future cards.I am struggle to understand what protocol I have to use to communicate with the card T0 or T1? So, correct me if I am wrong, but the reader actually decides by itself what protocol to use to communicate with the card if the card supports both.In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816 -4 Organization, security and commands for interchange . The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports all ISO 7816, EMV™, and GSM11-11 requirements. This one mixed-signal peripheral manages all the details of the interface between a microcontroller and two, independent smart cards.
The ISO 7816 standard defines the necessary protocols to communicate with a smart card. Although the communication software is tested with TimeCOS, the basic communication protocol (ISO 7816, T = 0) implemented in this application note is common with all smart cards. 2012 Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
I have also an ACR38 smart card reader that it support both T=0 and T=1 protocols. (I have T=0 communication with one card successfully and T=1 communication with this card successfully.) I wrote the below program and upload it on the card to send and receive extended APDUs: private ExAPDU() {.
Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is a standardized data format and communication protocol used in the interaction between smart cards - in our case, NFC tags - and card readers or host systems.In the context of smart cards, an Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is the unit of communication between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4, which specifies organization, security, and commands for .
Smart card application protocol data unit
Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level
If the card is able to process more than one protocol type and if one of those protocol types is indicated as T=0, then the protocol type T=0 shall indicated in TD1 as the first offered protocol, and is assumed if no PTS is performed. This application note describes the fundamentals of the contact type smart cards, and how they are communi-cated using the PIC microcontroller. It also explains the T = 0 and T = 1 protocols, which are widely used in contact type smart card communications.

passive rfid tag schematic diagram
passive rfid tags that work with standard wifi
Best printer to print on NFC cards? As you’ve discovered, it very much .
smart card protocol t1|Smart Card Reader T0 T1 communication on APDU level