how small can an rfid chip be Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips. Learn about Texas A&M, the state's first public university, and its mission, values, history, leadership and impact. Explore our academic programs, research, traditions, global engagement and more.
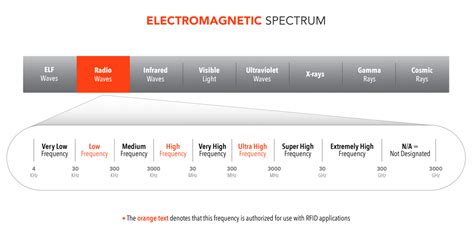
0 · Types of RFID Chips
1 · Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID
2 · RFID Chips Selection Guide: Types, Features, Applications
3 · RFID 'Powder'
4 · How Small Can An RFID Chip Be
Try the phone App first to get the hang of it. Easier for testing and understanding the whole .
Read range: Miniaturizing RFID chips can limit their read range, which refers to . Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies. Read range: Miniaturizing RFID chips can limit their read range, which refers to the distance between the chip and the RFID reader for effective communication. Smaller chips may have a shorter read range, requiring them to be in closer proximity to the reader.Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips.
Researchers have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip's design makes it possible to. “As far as we can tell, it’s the world’s smallest Gen2-compatible RFID chip,” according to Paul Franzon, a professor of electrical engineering at North Carolina State University. He was talking about a 125 x 245μm integrated circuit die presented at the IEEE International Conference on RFID.
Engineers at Columbia University have developed the smallest single-chip system ever created, which can be implanted with a hypodermic needle to measure temperature inside the body, and. Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags.The Japanese giant Hitachi has developed the world’s smallest and thinnest Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) chip. Measuring only 0.15 x 0.15 millimeters in size and 7.5 micrometers thick, the wireless chip is a smaller version of the previous record holder – . Researchers at Stanford University are currently working to create an RFID small enough to be inserted into a human cell. So far, the research team has been able to scale the chip and antenna down to 22 microns wide – one fifth the diameter of a human hair – and even embed it in the melanoma cell of a mouse.
Small size: Small RFID chips are usually between 1 and 2 cm in size and are suitable for scenarios that require smaller tags, such as retail merchandise management, tickets and smart cards. Small chips are slightly inferior to standard size chips in reading distance and signal stability, but can still meet most application requirements. Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies. Read range: Miniaturizing RFID chips can limit their read range, which refers to the distance between the chip and the RFID reader for effective communication. Smaller chips may have a shorter read range, requiring them to be in closer proximity to the reader.Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips.
Researchers have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip's design makes it possible to.
Types of RFID Chips
Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID
“As far as we can tell, it’s the world’s smallest Gen2-compatible RFID chip,” according to Paul Franzon, a professor of electrical engineering at North Carolina State University. He was talking about a 125 x 245μm integrated circuit die presented at the IEEE International Conference on RFID. Engineers at Columbia University have developed the smallest single-chip system ever created, which can be implanted with a hypodermic needle to measure temperature inside the body, and.
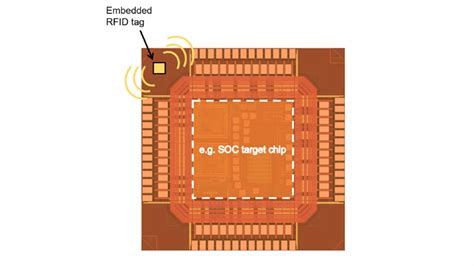
Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags.
The Japanese giant Hitachi has developed the world’s smallest and thinnest Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) chip. Measuring only 0.15 x 0.15 millimeters in size and 7.5 micrometers thick, the wireless chip is a smaller version of the previous record holder – . Researchers at Stanford University are currently working to create an RFID small enough to be inserted into a human cell. So far, the research team has been able to scale the chip and antenna down to 22 microns wide – one fifth the diameter of a human hair – and even embed it in the melanoma cell of a mouse.

RFID Chips Selection Guide: Types, Features, Applications

advantages of smart card in e commerce
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled .
how small can an rfid chip be|Smaller Chips Open Door to New RFID