effect of topology on indoor tracking using rfid In this project, we implemented an RFID-based mobile object tracking system on Qualnet simulator and studied two challenging problems in applying RFID into a tracking system—(i) anti-collision and high-speed identification of . I use a MIFARE Classic NFC access card. Is there any way to clone my card on an Android device (e.g. on Samsung Galaxy Nexus or Asus Nexus 7)? Note: this question is .With the advent of technology, it is now possible to copy an NFC card to your phone. This can be done with the help of Rango NFC, provided your device is rooted. To clone a card, hold the card you want to clone against your phone .
0 · Survey of Indoor Localization Based on
1 · RFID Indoor Tracking System Based on
2 · Optimizing indoor localization precision: advancements in RFID
3 · Optimizing indoor localization precision:
4 · Indoor mobile object tracking using RFID
5 · Indoor mobile object tracking using RFI
6 · Indoor Tracking With RFID Systems
NFC mobile payment app. Save you card track data and pay in shops with contactless card readers using your mobile phone. Add the cards using a mini magnetic stripe reader in your phone, or paste the track data into .
Survey of Indoor Localization Based on
what is family card number in smart card
RFID Indoor Tracking System Based on
Within the array of localized objects, we can randomly select a single object for the explicit purpose of tracking. The depiction of the RFID tag/object localization using the devised system is presented in figure 6. It was observed that as the tracked object moves farther from the RFID . In this project, we implemented an RFID-based mobile object tracking system on .Within the array of localized objects, we can randomly select a single object for the explicit purpose of tracking. The depiction of the RFID tag/object localization using the devised system is presented in figure 6. It was observed that as the tracked object moves farther from the RFID antenna, there is a noticeable decline in signal strength.
In this project, we implemented an RFID-based mobile object tracking system on Qualnet simulator and studied two challenging problems in applying RFID into a tracking system—(i) anti-collision and high-speed identification of .The ability to determine the spa-tial location of units belonging to a RFID technology is a starting point toward the development of sophisticated applications, such as people tracking for civil protec-tion, patients monitoring in hospitals, and quick rescuing of victims [3].This study comprehensively examines the current state of deep learning (DL) usage in indoor positioning. It emphasizes the significance and efficiency of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs).

This paper addresses the problem of indoor tracking of tagged objects with Ultra High Frequency (UHF) Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems. A new and more realistic observation model of the system is proposed, where the probability of detecting a tag by a reader is described by a Beta distribution. We model the probability of detection . Through the deployment of RFID reader and the indoor topology, a reflex and removal algorithm is designed which is based on the accessibility of the time limit, to reduce the effect of reflected problems on the RFID data.
what is not a benefit of smart card technology
Here, we investigate the use of Kalman filter to improve the precision and RFID map matching to improve the accuracy. Results obtained after simulations demonstrate the validity and suitability of the proposed algorithm to provide high performance level in terms of accuracy and scalability. The use of this indicator, derived from a time series of GNSS statistics, seeks to improve the selection criteria between using the GNSS-based or the VIO-based solution in each epoch, thus aiming to enhance the overall accuracy of . This paper presents a graph model based approach to indoor tracking that offers a uniform data management infrastructure for different symbolic positioning technologies, e.g., Bluetooth and RFID.The Traditional RFID indoor positioning algorithm LANDMARC utilizes a Received Signal Strength (RSS) indicator to track objects. However, the RSS value is easily affected by environmental noise and other interference.
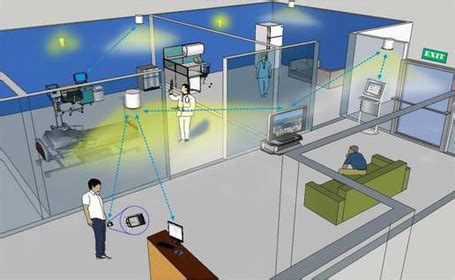
Within the array of localized objects, we can randomly select a single object for the explicit purpose of tracking. The depiction of the RFID tag/object localization using the devised system is presented in figure 6. It was observed that as the tracked object moves farther from the RFID antenna, there is a noticeable decline in signal strength. In this project, we implemented an RFID-based mobile object tracking system on Qualnet simulator and studied two challenging problems in applying RFID into a tracking system—(i) anti-collision and high-speed identification of .The ability to determine the spa-tial location of units belonging to a RFID technology is a starting point toward the development of sophisticated applications, such as people tracking for civil protec-tion, patients monitoring in hospitals, and quick rescuing of victims [3].
This study comprehensively examines the current state of deep learning (DL) usage in indoor positioning. It emphasizes the significance and efficiency of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs).
This paper addresses the problem of indoor tracking of tagged objects with Ultra High Frequency (UHF) Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems. A new and more realistic observation model of the system is proposed, where the probability of detecting a tag by a reader is described by a Beta distribution. We model the probability of detection .
Through the deployment of RFID reader and the indoor topology, a reflex and removal algorithm is designed which is based on the accessibility of the time limit, to reduce the effect of reflected problems on the RFID data.
Here, we investigate the use of Kalman filter to improve the precision and RFID map matching to improve the accuracy. Results obtained after simulations demonstrate the validity and suitability of the proposed algorithm to provide high performance level in terms of accuracy and scalability.
The use of this indicator, derived from a time series of GNSS statistics, seeks to improve the selection criteria between using the GNSS-based or the VIO-based solution in each epoch, thus aiming to enhance the overall accuracy of . This paper presents a graph model based approach to indoor tracking that offers a uniform data management infrastructure for different symbolic positioning technologies, e.g., Bluetooth and RFID.

$23.00
effect of topology on indoor tracking using rfid|Optimizing indoor localization precision: