read rfid at a distance The read range of RFID tags refers to the maximum distance at which the readers can successfully capture the data from the tags. Understanding the read range is crucial for implementing RFID systems effectively and optimizing their performance. I also have the same issue eff 11/15/23, a couple times, but have no smart watch or other device connected except some blue tooth headphones. NFC is not on. S21 Ultra 5G, One UI version 5.1, Android version 13. Did install a security .
0 · rfid tracking distance
1 · rfid reading distance
2 · rfid long distance
3 · rfid distance sensor
4 · rfid distance reader
5 · low frequency rfid range
6 · long range rfid tracking
7 · long distance rfid scanner
The document suggests that background NFC tag reading is supported only by the new iPhone Xs, Xs Max and Xr: “iPhone X and earlier devices don’t support background tag reading.”. According to the iPhone .
The read range of RFID tags refers to the maximum distance at which the readers can successfully capture the data from the tags. Understanding the read range is crucial for implementing RFID systems effectively and optimizing their performance.High frequency (HF) RFID chip. Typical frequency is 13.56 MHz, reading distance distances from a few centimeters to several meters. Suitable for medium-distance application scenarios, such .
The read range of RFID tags refers to the maximum distance at which the readers can successfully capture the data from the tags. Understanding the read range is crucial for implementing RFID systems effectively and optimizing their performance.High frequency (HF) RFID chip. Typical frequency is 13.56 MHz, reading distance distances from a few centimeters to several meters. Suitable for medium-distance application scenarios, such as payment system and identification.RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions.
The distance from which a tag can be read is called its read range. Read range depends on a number of factors, including the frequency of the radio waves uses for tag-reader communication, the size of the tag antenna, the power output of the reader, and whether the tags have a battery to broadcast a signal or gather energy from a reader and .Passive low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) tags can be read from a distance of up to 3 feet (0.9 meter), while passive ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) RFID transponders can typically be read from 10 to 20 feet (3 to 6 meters) away.
Unlike barcodes, which require direct line-of-sight scanning, RFID tags can be read from a distance and even through materials such as fabric, plastic, or cardboard. This makes them ideal for inventory management, supply chain tracking, asset tracking, access control, and many other applications.
Even within one type of RFID, however, there can be a wide array of read ranges. A passive ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) handheld reader has a range of about 10 feet, while a model using a beam-steerable phased-array antenna can interrogate passive tags at . Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data.RFID tags with different distance ranges have their advantages in various application scenarios. Understanding and grasping the differences in these reading ranges is crucial for selecting and optimizing RFID systems.
Read range is the distance from which an RFID tag can be detected. The read range expresses the distance from which the tag receives just enough power to be activated to send back a signal to the reader.
The read range of RFID tags refers to the maximum distance at which the readers can successfully capture the data from the tags. Understanding the read range is crucial for implementing RFID systems effectively and optimizing their performance.High frequency (HF) RFID chip. Typical frequency is 13.56 MHz, reading distance distances from a few centimeters to several meters. Suitable for medium-distance application scenarios, such as payment system and identification.RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions.The distance from which a tag can be read is called its read range. Read range depends on a number of factors, including the frequency of the radio waves uses for tag-reader communication, the size of the tag antenna, the power output of the reader, and whether the tags have a battery to broadcast a signal or gather energy from a reader and .
Passive low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) tags can be read from a distance of up to 3 feet (0.9 meter), while passive ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) RFID transponders can typically be read from 10 to 20 feet (3 to 6 meters) away.
Unlike barcodes, which require direct line-of-sight scanning, RFID tags can be read from a distance and even through materials such as fabric, plastic, or cardboard. This makes them ideal for inventory management, supply chain tracking, asset tracking, access control, and many other applications.Even within one type of RFID, however, there can be a wide array of read ranges. A passive ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) handheld reader has a range of about 10 feet, while a model using a beam-steerable phased-array antenna can interrogate passive tags at . Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data.
RFID tags with different distance ranges have their advantages in various application scenarios. Understanding and grasping the differences in these reading ranges is crucial for selecting and optimizing RFID systems.

rfid tracking distance
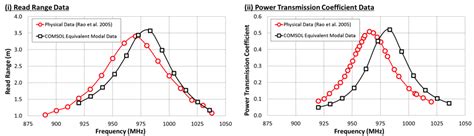
passive rfid tags have a range from ______ to ______
paypal debit card rfid
How to Scan NFC (iPhone XR, XS and newer) Watch on. Locate where the NFC tag is located on the object you are scanning. Tap the top of your iPhone to where the NFC tag is located on the object. Upon read a notification .Posted on Nov 1, 2021 12:10 PM. On your iPhone, open the Shortcuts app. Tap on the Automation tab at the bottom of your screen. Tap on Create Personal Automation. Scroll down and select NFC. Tap on Scan. Put .
read rfid at a distance|low frequency rfid range