rfid chip cells Researchers have created radio-frequency tags that can fit inside single cells and that could one day help analyze diseases. Sat, Jan 5, 2013. Vikings. 10. Packers. 24. Final. The Washington Redskins were defeated by the Seattle Seahawks, 24 to 14, in the 2012 NFC Wild Card game on January 6, 2013.Within each conference, the four division winners and the top two non-division winners with the best overall regular season records) qualified for the playoffs. The four division winners are seeded 1–4 based on their overall won-lost-tied record, and the wild card teams are seeded 5–6. The NFL does not use a . See more
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · what makes something rfid
2 · what does rfid look like
3 · types of rfid chips
4 · rfid is involved when using
5 · rfid for personal use
6 · how does rfid scanning work
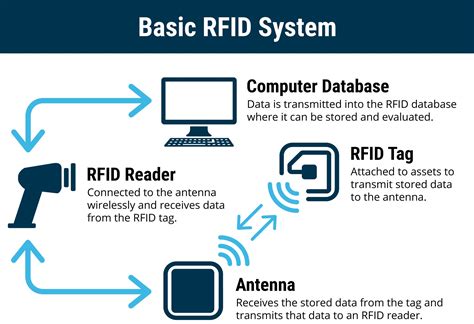
7 · how do rfid chips work
Get the latest 2024 NFL Playoff Picture seeds and scenarios. See the full NFL conference .
Researchers have created radio-frequency tags that can fit inside single cells and that could one day help analyze diseases. We demonstrate that a 25 \ (\upmu \) m wireless radio frequency identification (RFID) device can not only be taken up by a mammalian cell but can also be detected and specifically. Researchers have created radio-frequency tags that can fit inside single cells and that could one day help analyze diseases.Stanford University researchers have now developed a tiny wireless chip that can go inside the cell to report evidence on some of those mysteries. A team led by electrical engineers Ada Poon and H.S. Philip Wong has created a chip system based on radio frequency identification device (RFID) technology, similar to the RFID tags found on .
Medical devices that can be ingested or implanted in the body could offer doctors new ways to diagnose, monitor, and treat many diseases. Traverso’s lab is now working on a variety of ingestible systems that can be used to deliver drugs, monitor vital signs, and detect movement of the GI tract. Researchers want to use radio frequency identification (RFID) chips for keeping track of organoids, samples of human tissue that mimic pieces of organs and are grown from stem cells. Researchers at Stanford University are now several phases into a development project to create a passive, 60 GHz RFID transponder that is small enough to be inserted into a human body’s cell. Thus far, the group has been able to scale the chip and antenna down to about 22 microns (0.0009 inch) wide—one fifth the diameter of an average human .A passive RFID microchip absorbs energy from an external source and emits a radiofrequency identification signal which is then decoded by a detector. In the present study, we investigated the effect of the radiofrequency energy emitted by a RFID microchip on human cancer cells.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. Passports and some credit cards have RFID chips that allow information to be read wirelessly. An industry has sprung up to make wallets and other products that block hackers from "skimming" the. Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies.
We demonstrate that a 25 \ (\upmu \) m wireless radio frequency identification (RFID) device can not only be taken up by a mammalian cell but can also be detected and specifically. Researchers have created radio-frequency tags that can fit inside single cells and that could one day help analyze diseases.Stanford University researchers have now developed a tiny wireless chip that can go inside the cell to report evidence on some of those mysteries. A team led by electrical engineers Ada Poon and H.S. Philip Wong has created a chip system based on radio frequency identification device (RFID) technology, similar to the RFID tags found on .
Medical devices that can be ingested or implanted in the body could offer doctors new ways to diagnose, monitor, and treat many diseases. Traverso’s lab is now working on a variety of ingestible systems that can be used to deliver drugs, monitor vital signs, and detect movement of the GI tract. Researchers want to use radio frequency identification (RFID) chips for keeping track of organoids, samples of human tissue that mimic pieces of organs and are grown from stem cells. Researchers at Stanford University are now several phases into a development project to create a passive, 60 GHz RFID transponder that is small enough to be inserted into a human body’s cell. Thus far, the group has been able to scale the chip and antenna down to about 22 microns (0.0009 inch) wide—one fifth the diameter of an average human .A passive RFID microchip absorbs energy from an external source and emits a radiofrequency identification signal which is then decoded by a detector. In the present study, we investigated the effect of the radiofrequency energy emitted by a RFID microchip on human cancer cells.

where are rfid chips used
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. Passports and some credit cards have RFID chips that allow information to be read wirelessly. An industry has sprung up to make wallets and other products that block hackers from "skimming" the.

flash memory card for smart phone

what makes something rfid
$18.70
rfid chip cells|how does rfid scanning work